As we begin the new year, it’s a great time to revisit some of the most popular blogs we published in 2023. Our top blogs from last year covered a range of topics, including a cybersecurity outlook, updated third-party risk management guidelines, using conditional access policies (CAPs) and multifactor authentication (MFA) to enhance security within Microsoft Azure Active Directory (AD), and NetConnect 2023. If you didn’t have a chance to read these posts—or simply want to review them—here is a recap of each of them. They offer unique perspectives, best practices, and a wealth of insights that can help your financial institution prepare for greater success in the year ahead.
2023 Cybersecurity Outlook for Community Banks and Credit Unions
Safe Systems’ 2023 Cybersecurity Outlook for Community Banks and Credit Unions revealed valuable peer-to-peer insights that can help financial institutions enhance their security posture. The survey highlights cyber preparedness and budget restraints as top security challenges of more than 50% of the 160 participating financial institutions. It also shared participants’ feedback on other important areas, including prevention and detection security layers; employee security awareness training and testing; and advanced firewall features. For instance, respondents use multiple layers of security, but less than 50% of them combine every security layer listed in the survey. Survey respondents also use a variety of security training—including resource-intensive individual instruction. In addition, most of the survey participants are taking advantage of advanced firewall features, although only 24% of 135 respondents leverage sandboxing technology to detect threats. Read more.
Updated Regulatory Guidelines on Third-Party Risk Management
In June, federal bank regulatory agencies issued updated guidelines to make it easier for financial institutions to manage third-party risks. This new guidance from the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), and Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) impacts all banking institutions that use third parties. The majority of statements in the new guidance focus on the planning, due diligence, and contract phases with an emphasis on pre-engagement. Since auditors and examiners will be looking more closely at what happens during the pre-engagement stage, institutions need to place more emphasis on scrutinizing potential third parties. Not all statements in the guidance will apply to all institutions or relationships, so we have developed an interactive checklist designed to walk you through key regulatory requirements of the third-party relationship life cycle. Read more.
Using CAPs and MFA to Enhance Security within Microsoft Azure AD
There was a surge in successful phishing campaigns last year, including sophisticated schemes that were able to bypass MFA. MFA-resistant phishing is a significant threat since this type of attack could impact a vast segment of organizations that rely on Microsoft Azure AD (now known as Microsoft Entra ID) and Microsoft M365 services to support their operations. However, financial institutions can use a variety of measures to prevent cyberattacks, including Conditional Access Policies (CAPs). CAPs, which are foundational to safeguarding identities within Microsoft Entra ID, protect the initial step of the identification chain—the sign-in attempt. To maximize protection, institutions should stack multiple CAPs, such as requiring MFA, denying sign-ins from outside of the USA, and requiring device compliance. When designing CAP logic, they should take a broad approach to the scope of the CAP to impact as many areas as possible. Institutions can take a multi-layered approach to optimizing security by leveraging multiple security tactics, technologies, and resources. Read more.
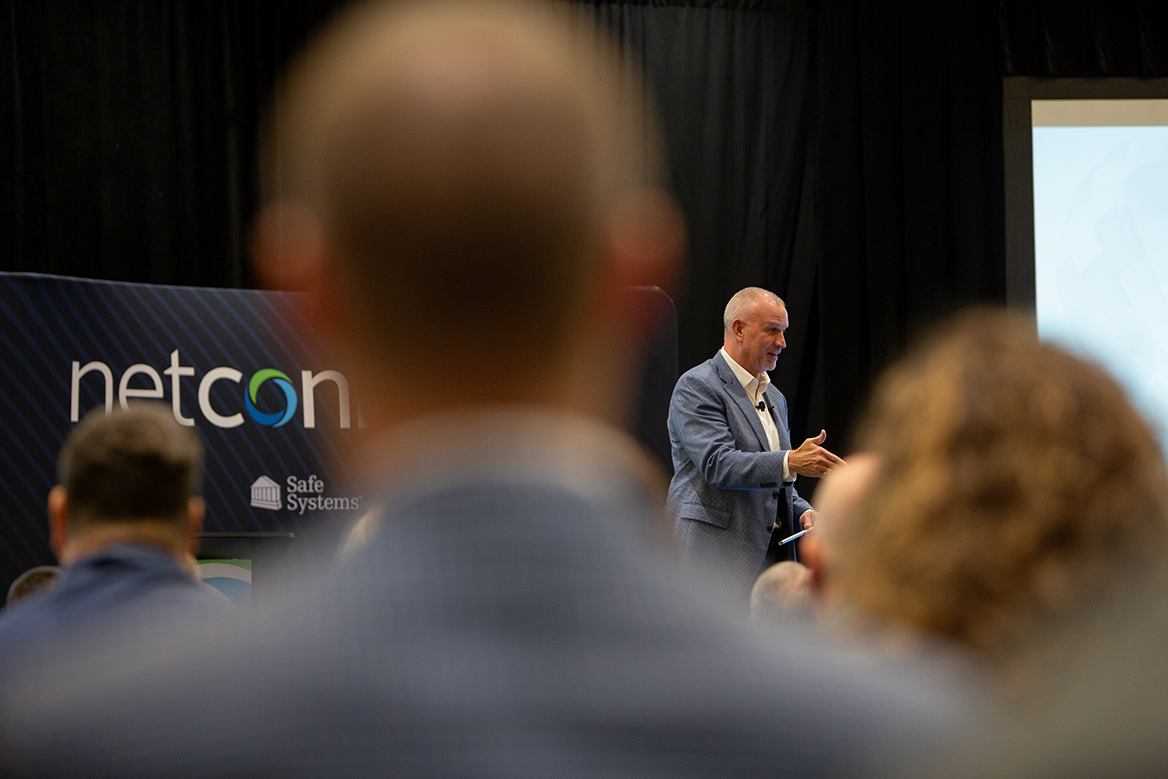
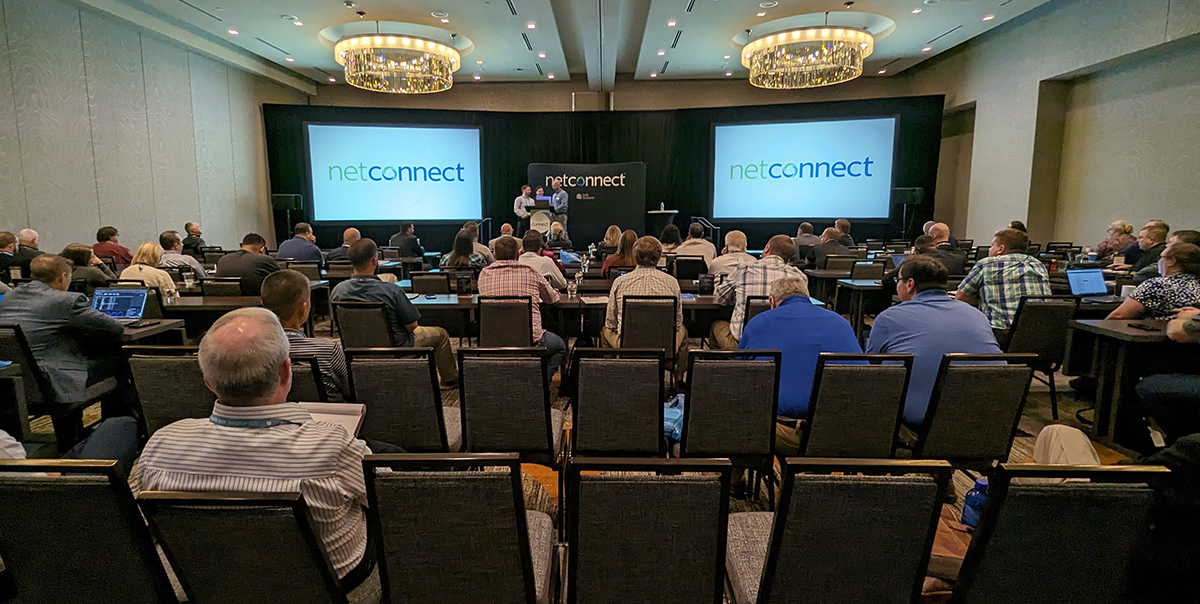
NetConnect 2023—A Glimpse into the Future of Technology and Compliance
The 2023 NetConnect Customer User Conference brought Safe Systems’ customers, employees, and partners together in Alpharetta, Ga. to discuss banking industry trends, challenges, and innovations. NetConnect 2023 provided valuable insights into banking and technology’s vital role in shaping the industry’s future. With multiple informative sessions, the conference covered the significance of hope in business, changes relating to regulatory compliance, vulnerability management, and Microsoft Azure fundamentals. Read more.
Get the latest industry developments, insights, and trends delivered directly to your inbox. Subscribe now to the Safe Systems blog.







































































 Keith Haskett is the president and CEO of Rebyc Security and is responsible for executing their strategic plan. After several years leading the Risk and Information Security Consulting Services practice at CSI, he co-founded Rebyc to deliver offensive security solutions customized to meet the needs of the highly regulated, financial services industry. His teams have delivered over 2,000 engagements to financial institutions nationwide.
Keith Haskett is the president and CEO of Rebyc Security and is responsible for executing their strategic plan. After several years leading the Risk and Information Security Consulting Services practice at CSI, he co-founded Rebyc to deliver offensive security solutions customized to meet the needs of the highly regulated, financial services industry. His teams have delivered over 2,000 engagements to financial institutions nationwide.






























