Your Guide to Business Continuity Management and Disaster Recovery Planning
Overview
Businesses today encounter an ever-increasing volume of operational threats, so it’s critical for banks and credit unions to have adequate business continuity and disaster recovery (DR) procedures in place. Business continuity management (BCM) entails all aspects of incorporating resilience, incident response, crisis management, vendor management, disaster recovery, and business process continuity—and it can enable an institution to keep operating if a disruption such as a cyberattack, natural disaster, or man-made event occurs.
We understand that BCM and DR planning can be challenging, so this guide provides some key strategies and best practices to help financial institutions execute them successfully.
BCP vs. DR: Key Differences
It is first important to understand the key differences between a business continuity plan (BCP) and a disaster recovery plan as these two terms are often mistakenly used interchangeably. The Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) updated its Business Continuity Management IT Examination Handbook a few years ago to expand its focus from “business continuity planning” to “business continuity management.” The BCM process is one in which a financial institution must proactively plan for resiliency to disruptive events and recover from those events. The traditional business continuity plan is now a subset of the overall BCM process and will be referred to as business continuity management plan (BCMP) going forward. The BCMP outlines what needs to happen to ensure that key products and services continue to be delivered in case of a disaster. On the other hand, the DR plan outlines the specific steps to be taken to recover the interdependencies the institution must restore to return to normal operations after a disaster. The BCMP focuses on the continuation of critical functions, while the DR plan focuses on the restoration and recovery of the specific individual technology and third-party components necessary for those functions.
BCMP: A plan to continue the business operations necessary to ensure key products and services are delivered
DR: A plan for accessing required technology, infrastructure, and third-party components after a disaster
In the previous guidance, business continuity and disaster recovery were closely tied together, but the new guidance defines them as two separate concepts and states that “The business strategy, not technology solutions, should drive resilience.” It places a heavy focus on resilience and states that financial institutions cannot rely on technology alone to ensure resilience. Although technology can help provide resilience and offer significant advantages to your recovery capabilities, indeed in many cases technology could be what failed in the first place. Financial institutions must be able to offer products and services to their customers or members regardless of technology or third-party failure, and often that could mean using manual processes and procedures to accomplish this.
Finally, the latest BCMP guidance provided an important distinction between a “test” and an “exercise.” Simply put, a test focuses on demonstrating the resilience and recovery capabilities of your systems, and an exercise addresses the people, processes, and procedures. For example, where a test may focus on backup and recovery options of systems, data restoration, device replication and rebuild or replacement, an exercise would verify that your staff (and ideally third parties) are aware of and could execute those options effectively. Both exercises and tests are now a requirement, and together they provide a high degree of confidence that your recovery procedures will allow you to meet your pre-determined process for recovery time objectives (RTOs).
Business Continuity Management Planning
Business continuity management is an essential system for preventing and recovering from potential threats. As a part of the business continuity process, a compliant and successful BCMP should include risk management (business impact analysis and risk/threat assessment); continuity strategies (interdependency resilience, continuity, and recovery); training and testing (exercises); maintenance and improvement; and board reporting.
What CEOs Should Know about BCMP
To adhere to regulatory guidance, it is imperative for institutions to not only comprehend the entire business continuity management program but also employ a broad process-oriented approach that considers technology, business operations, testing, and communication strategies that are necessary for the entire organization—not just the information technology department.
Management should develop BCMPs with sufficient detail appropriate to the institution’s size and complexity. According to FFIEC guidance, “The BCMP should address key business needs and incorporate inputs from all business units.” The institution’s business continuity management program should align with its strategic goals and objectives. In addition, management should consider the entity’s role within and impact on the overall financial services sector when developing the program.
Key Steps to Developing a Compliant BCMP
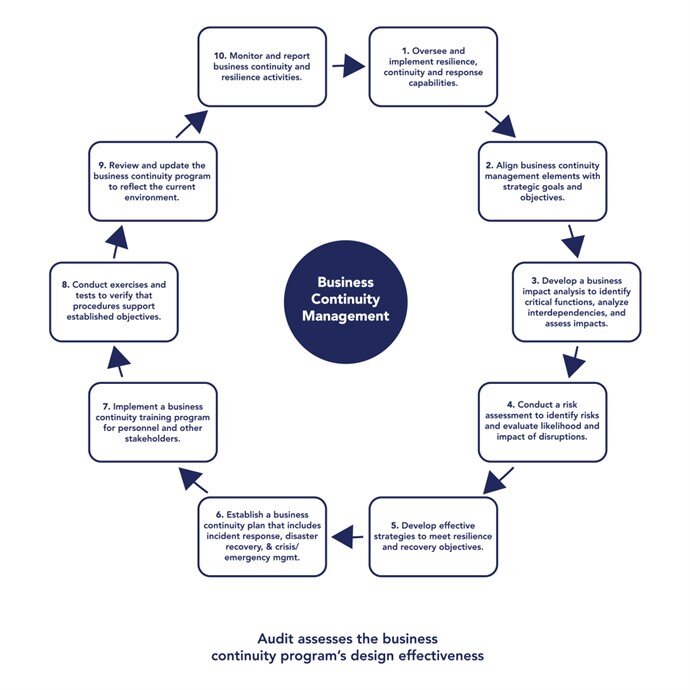
To develop a successful, compliant BCMP, it is important to understand and follow the recent, more detailed view of the BCM lifecycle in the FFIEC Business Continuity Management IT Examination Handbook. This approach is a bit more complicated than the process has been in the past and may require more time for plan preparation and annual maintenance. Here is a checklist consisting of the required elements of the new approach that may not be incorporated into your current program:
- Have you conducted a formal business process-based Business Impact Analysis (BIA) that identifies all critical interdependencies?
- Does the BIA produce sufficient information to establish the following?
- Recovery point objectives (RPO)
- Recovery time objectives (RTOs) for each business process (prioritized)
- Maximum tolerable (or allowable) downtime (MTD/MAD)
- Does your risk/threat assessment measure both the impact and the probability (likelihood) of potential disruptive threats, including worst-case (low probability, high impact) scenarios?
- Do you use testing as employee training exercises to verify that personnel is knowledgeable of recovery priorities and procedures?
- Do you track and resolve all issues identified during testing exercises and use lessons learned to enhance your program? (Must be documented.)
- Does your board report include a written presentation providing the BIA, risk assessment, and exercise and test results, including any identified issues?
Tactics for Staying Ahead of Regulators
Although there are several tips, tricks, and tactics to enhance compliance, one of the main tactics financial institutions can apply to stay ahead of regulators is to focus on resilience. Resilience includes the ability to anticipate, prepare for, prevent, and adapt to changing conditions, and to respond to, withstand, and recover rapidly from deliberate attacks, accidents, or naturally occurring threats or incidents. Management should incorporate the concept of resilience into all areas, including their business continuity management process, vendor management program, third-party supply chain management, and information security program. The objective is to implement processes to minimize the possibility of disruption and reduce the impact of such an event if it happens.
Inconsistencies between procedures and practices will often result in exam findings. Mentioning outdated references or older terminology in policies is one of the most common offenses that institutions commit. For instance, referencing business continuity plan or planning (BCP) versus business continuity management plan or planning (BCMP). This would be a minor mistake because the term BCP is not necessarily obsolete, but it’s not consistent with the most recent guidance and could raise a “red flag” that leads examiners to wonder if the institution has properly updated its policies, resulting in further scrutiny. A tactic that financial institutions can use to minimize outdated references and other inconsistencies between procedures and practices is to implement automation. Technology can make it easier for institutions by providing regular updates to accommodate changing regulations and trends as well as make it more feasible for them to identify inconsistencies between their policies and procedures.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Disaster recovery—the process of restoring IT infrastructure, data, and third-party systems—should address a broad range of adverse events such as natural disasters, infrastructure failures, technology failures, unavailability of staff, or even cyberattacks. As part of the disaster recovery strategy, management should identify key business processes and activities to be maintained while IT systems and applications are unavailable and prioritize the order in which these systems are restored, which should be reflected in the business impact analysis. The FFIEC’s Business Continuity Management IT Examination Handbook states:
“Management should develop a coordinated strategy for the recovery of data centers, networks, servers, storage, service monitoring, user support, and related software… Disaster recovery should address guidelines for returning operations to a normalized state with minimum disruption.”
What CEOs Should Know about DR
Here are some important DR considerations for CEOs to consider to ensure their institution is taking an effective approach to disaster recovery:
- Expect the Unexpected: A disaster can strike anytime and in a myriad of ways. Most people think of a disaster as being a situation created by an unexpected weather event, power outage, equipment failure, or cyberattack, but network downtime due to human error is also a common cause of disruption. The need for disaster recovery is a matter of when—not if. Therefore, CEOs should expect some type of disaster to affect their institution.
- Be Proactive: Not having a sufficient disaster recovery plan in place can have major negative consequences: a loss of data, business functions, clients, and reputation—not to mention time and money. So, bank CEOs must ensure their management team is being preemptive about implementing effective disaster recovery strategies. These strategies should be reflected in the BIA, which can reveal gaps in critical processes that would hinder the institution’s disaster recovery and, in turn, business continuity.
- Consider Outsourcing: More than one-third of small and medium-sized businesses do not have a plan in place for responding to data breaches and cyberattacks, according to the Ponemon Institute’s 2019 Global State of Cybersecurity in Small and Medium-Sized Businesses report. However, bank management can leverage external resources to expand their institution’s disaster recovery capabilities. Outside vendors can provide new technologies that reduce risk and enhance data backup, storage, and recovery. They offer a variety of cloud-based solutions that can make the DR process more streamlined, efficient, and cost-effective.
The 4Rs of DR Planning
For effective disaster recovery, there are four important “R’s” that institutions should focus on:
- Recovery time objective (RTO) – The longest acceptable length of time that a computer, system, network, or application can be down after a disaster happens. Shorter RTOs require more resources and ongoing expenses. When setting RTOs, prioritizations must be made based on the significance of the business function and budgetary constraints.
- Recovery point objective (RPO) – The amount of time between a disaster occurring and a financial institution’s most recent backup. If too long, and too much data is allowed to be lost, it could result in substantial damage. Essentially, the RPO will be determined by the institution’s technology solution and risk tolerance.
- Replication – An exact copy of an institution’s data to be available and remotely accessible when an adverse event happens. The best practice is to have one backup onsite and another offsite in a different geographic region—somewhere that is not likely to be affected by the same disaster.
- Recurring testing – A variety of tests and exercises to verify the ability to quickly resume core business applications during a disaster situation. Thorough testing of a financial institution’s core applications should be done annually — while they are functioning normally — to generate the most meaningful feedback.
Why a Cloud DR Service Is Important
Institutions must have viable DR measures in place, and a comprehensive, cloud-based service is a cost-effective way to accomplish this. With DR in the cloud, institutions are always able to access their data—no matter what type of disaster happens. In addition, a cloud DR service offers a team of third-party experts who are available to advise on DR processes, ensure ongoing backups and regular testing are done in the correct timeframes, and serve as an extension of the staff when a disaster strikes.
A comprehensive cloud DR service offers substantial redundancy, reliability, uptime, speed, and value. In addition, a cloud DR solution from an outside service provider can give institutions peace of mind from knowing their DR plan is being adequately tested and will work during a real disaster.
Our Solutions
Safe Systems offers a wide range of comprehensive services to help community banks and credit unions support their BCM and DR planning and other efforts. Whether it’s compliance services, such as BCP Blueprint, Vendor Management, or Information Security Program, or technology services, such as Managed Site Recovery, Managed Cloud Services, or CloudInsight, institutions can customize solutions to meet their specific needs and budget.