The Ultimate Guide To Business Continuity Management for Banks and Credit Unions

By Tom Hinkel
In November 2019, the Federal Financial Institution Examination Council (FFIEC) updated its BCP IT Examination Handbook and expanded its focus from Business Continuity Planning (BCP) to Business Continuity Management (BCM). The change makes sense, because “planning” is only one part of the business continuity process. Business continuity management encompasses the entire process by integrating resilience, incident response, crisis management, third-party integration, disaster recovery, and business process continuity.
In the financial industry, community banks and credit unions are required to develop compliant business continuity plans that identify business processes along with their interdependencies that provide resilience to, and recovery from, all potential threats to the financial institution. BCM is designed to help organizations, regardless of their size, location or activity, minimize the impact of disruptions of any kind, natural or man-made, including cyber.
The new BCM guidance represents the first major update since 2015 and calls for all “entities” to rethink their approach to business continuity and be prepared to make appropriate plan revisions to meet these expectations. Entities are defined as depository financial institutions, nonbank financial institutions, bank holding companies, and third-party service providers. The use of this term is significant, as it essentially pulls all interdependencies into the planning process.
With so much at stake, it is important for financial institutions to understand the BCM process and the key requirements to develop the business continuity plan:
- Regulatory requirements relevant to a compliant BCM Program
- How to develop the business continuity management plan (BCMP)
- Pandemic planning and business continuity strategy
- The importance of integrating vendor management into the BCMP
- Steps to effectively update and test the plan
- The benefits of automating the BCM process
Regulatory Requirements
To comply with regulatory expectations, financial institutions are required to focus on an enterprise-wide, process-oriented approach that considers technology, business operations, testing, and communication strategies that are critical to business continuity management for the entire organization, not just the information technology department. Regulations make it clear that institutions need to plan to perform their critical business functions, even if technology may be impaired or unavailable.
Auditors and examiners are also scrutinizing business continuity plans to verify that the institution’s methodology and plan structure closely adhere to the 2019 regulatory guidance. A key change in the guidance is the increased focus on resilience. Resilience is the ability to prepare for—and adapt to—changing conditions and both withstand and recover rapidly from disruptions, whether that includes deliberate attacks, accidents or naturally occurring threats or incidents. Two keys for understanding resiliency are the terms “withstand” and “recover”, with an emphasis on withstanding adverse events. In the past, business continuity planning has been focused more on recovery, but now the FFIEC has placed a heavy focus on resiliency. The ultimate goal is for financial institutions to be more proactive and minimize having to implement traditional recovery measures down the road. When going through the BCM process, resilience must be included from the very beginning of the process to successfully meet regulatory expectations.
How to Develop a BCMP – What to Include in the Plan
It’s safe to say that most banks and credit unions have some sort of a BCMP in place, yet many struggle with determining what to include in the plan to ensure it is both recoverable and compliant. With the new changes to the guidance, many community banks and credit unions may also be wondering what specific changes they’ll need to make to meet these new expectations.
While each financial institution has a unique operating model based on its services, demographic profile, organizational processes, and technologies, the first step when drafting or updating the BCMP is to have a thorough understanding of all the functions and processes that make up those operations. This process, which we refer to as Enterprise Modeling, involves identifying all departments or functional units, with all associated processes and functions (including all internal and external interdependencies), and determining the team owners and members responsible for each department. Having representatives from each department take an active role in the planning process ensures the technologies and responsibilities for each area are accurately represented. This also helps the financial institution develop a more accurate assessment of its recovery time objectives and actual recovery capabilities. It is not realistic to have a single individual with all the knowledge and unique skill set required to put together a comprehensive BCMP.
A plan should consist of all the steps required to ensure key products and services remain available to customers or members. The BCMP consists of five phases including risk management (Business Impact Analysis, Risk/Threat Assessment); continuity strategies (Interdependency Resilience, Continuity and Recovery); training and testing (aka Exercises); maintenance and improvement; and board reporting.
Furthermore, the BCMP should be a “live” document that keeps pace with any changes in infrastructure, strategy, technology, and human resources. As soon as a plan is board approved, it should be tested, and a new draft plan should be initiated. At any point in time you should have both an approved plan, as well as a live draft to accommodate changes.
Pandemic Planning and Business Continuity Strategy
In the past, financial institutions were required to have a separate pandemic plan, but the new FFIEC guidance instead expects community banks and credit unions to assess and manage pandemic risk alongside all other possible disasters. This means the BCM plan is the pandemic plan, and financial institutions must analyze the impact a pandemic can have on the organization; determine recovery time objectives (RTOs); and build out a recovery plan.
As we’ve all learned, pandemic planning is very different from natural disasters, technical disasters, malicious acts, or terrorist events because the impact of a pandemic is much more difficult to determine due to the differences in scale and duration. Pandemics also directly impact financial institution and third-party employees rather than targeting infrastructure or technology-based interdependencies. Cross training and succession planning should be a key part of the pandemic planning process to ensure operations can continue even if key individuals are unavailable.
FFIEC guidance states that the financial institution’s BCMP should include five key elements to address the unique challenges posed by a pandemic event:
- A preventive program including monitoring of potential outbreaks; educating employees; communicating and coordinating with critical service providers and suppliers; and providing appropriate hygiene training and tools to employees
- A documented strategy that provides for scaling the institution’s pandemic efforts to align with the current six-stage CDC framework
- A comprehensive framework of facilities, systems, or procedures that provide the organization the capability to continue its critical operations in the event that large numbers of the institution’s staff are unavailable for prolonged periods
- A testing program to ensure that the institution’s pandemic planning practices and capabilities are effective and will allow critical operations to continue
- An oversight program to ensure ongoing review and updates to the pandemic plan
The Importance of Integrating Vendor Management into the BCMP
The vast majority of banks and credit unions today rely on third-party service providers, or vendors, to conduct business on a day-to-day basis. When financial institutions outsource key functions to a service provider, it creates a reliance on that third-party and exposes the institution to the risk of not being able to resume operations within pre-defined recovery time objectives in the event of a disruption. The FFIEC now expects critical third-party providers to be active participants in the BCM program, and it’s likely that regulators will require financial institutions to have a detailed understanding of the resilience capabilities of their core/technology service providers, cloud providers and others moving forward. When creating a BCMP, financial institutions have to account for all interdependent third-party relationships and identify the potential consequences a third-party disruption might have on its operations.
The criticality of the product or service the vendor provides is directly related to the criticality of the dependent process it supports, as identified by the business impact analysis. Some questions financial institutions should consider include:
- How important is this vendor to what we do?
- If they fail, how many of our dependent services would be negatively impacted?
- How challenging would it be to replace this vendor?
Vendor criticality is expressed in terms of Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs), and each bank or credit union determines and assigns the same RTOs to the third-party vendor as they have to the underlying process they support. In other words, if you’ve identified a two-day recovery time objective for a particular process, any underlying vendors will also inherit that same two-day RTO. In the event that the vendor cannot match your RTO (validated by testing), you must have a contingency plan in place such as alternative procedures or providers to compensate for the gap.
Successfully integrating vendor management and business continuity planning is essential for financial institutions to truly understand their actual recovery capabilities by validating whether or not their third-party providers “have sufficient recovery capabilities” to meet your recovery objectives.
Importance of Exercises and Tests When Updating the BCMP
Exercises and tests are important parts of the process, and in fact, the BCMP is not complete until the plan has been thoroughly tested. The new handbook makes an important distinction between exercises and tests in the BCMP process, defining an exercise as “a task or activity involving people and processes that is designed to validate one or more aspects of the BCMP or related procedures.” On the other hand, a test is often performed “to verify the quality, performance, or reliability of system resilience in an operational environment.” The handbook emphasizes the importance of both exercises and tests to demonstrate resilience and recovery capabilities.
Exercises and testing verify the effectiveness of the plan by validating all recovery time objectives; helps train the team on what to do in a real-life scenario; and identifies areas where the plan needs to be strengthened. In addition, examiners are also verifying that a BCMP has been tested, and the financial institution is able to execute the plan if and when the need arises. Because the financial industry is considered part of the nation’s critical infrastructure, testing, exercises, and training will continue to be a focus going forward.
Every test should start with a realistic scenario drawn from the top threats as identified by the risk management phase of the planning process. Top threats are those determined to have both high impact and high probability ratings. While initial testing of a plan can be relatively straightforward, a bank or credit union should strive to extend the scope and severity of the exercise with each consecutive test by making the tests consecutively more complex and including different individuals. Conducting the very same test with the same participants every year will not satisfy examiners nor will it give your management the assurance they need.
In addition to the senior management and information security roles defined in a plan, the testing team should include key department heads with detailed knowledge of the processes and functions impacted by the scenario. Tests should cover the steps departmental managers must take to complete functions manually or in an alternate way. In addition, all departmental specialists should be included in the exercise and testing program. There are two reasons for that, the first is so they are familiar with alternate procedures in emergency scenarios, the second is to make sure you have backups, or successors, to your primary recovery resources. Succession planning is another hot button item with examiners now because of the pandemic.
While regulators require proof of exercises and testing annually, more frequent testing is indicated whenever a previous test uncovered significant gaps in the plan, or if there are significant internal changes to processes or infrastructure or personnel.
Automating the Planning Process
To help streamline this time-consuming process, banks and credit unions can automate repetitive portions of business continuity planning. Automating these activities eliminates the need to update cumbersome spreadsheets and manually copy/paste information from various reports and previous assessments. The 2019 guidance requires a number of changes to your existing plan, some subtle and some significant.
An automated BCP solution will also help guide banks and credit unions through the entire BCMP process, assuring that all required elements are included as they are necessitated by regulatory guidance changes. Automating the planning process makes it easier and much less time-consuming to perform annual plan updates by allowing static portions of the plan to carry forward, while incorporating changes wherever necessary. Any automated solution should also allow you to identify all material plan changes from year-to-year, so management and board approval is easier.
Conclusion
Business Continuity Management is a critical process for banks and credit unions regardless of size and location, and the plan is central to that effort. To streamline the planning process, financial institutions should integrate business continuity into all business decisions; conduct periodic reviews of the plan; and perform regular testing. Everyone in the organization — from the tellers to the Board — should understand the importance of business continuity planning and how his or her unique role fits into the financial institution’s overall business continuity strategy.

















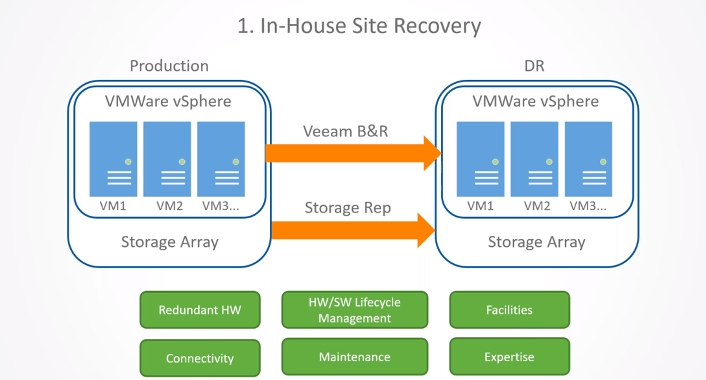
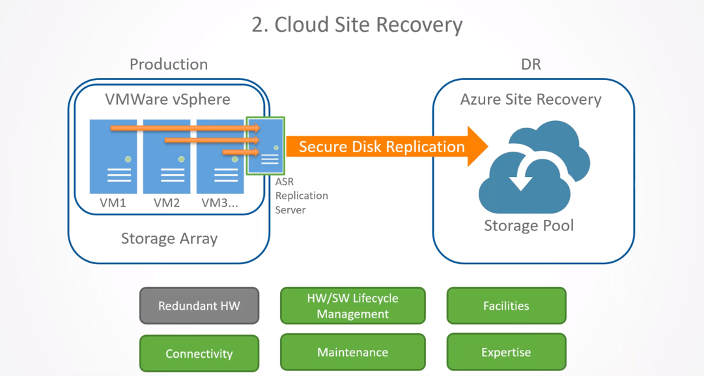
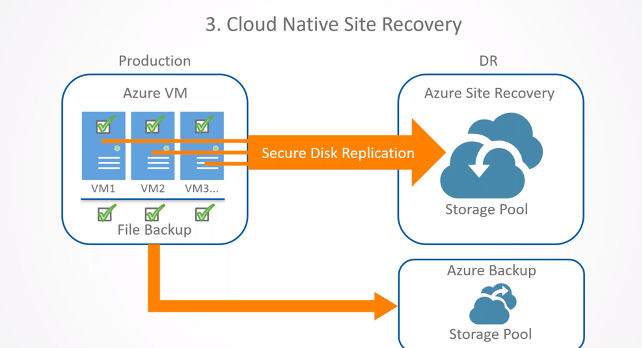





























 Using Continuum, Safe Systems established a site-to-site Virtual Private Network (VPN) between the branch in Blairsville and the Continuum site hosting the recovered servers to get operations back up and running quickly. Displaced employees could remotely access the network, and the bank was able to leverage Continuum for two full days until power was restored at all branches and the production servers were powered back on.
Using Continuum, Safe Systems established a site-to-site Virtual Private Network (VPN) between the branch in Blairsville and the Continuum site hosting the recovered servers to get operations back up and running quickly. Displaced employees could remotely access the network, and the bank was able to leverage Continuum for two full days until power was restored at all branches and the production servers were powered back on. 


 Aside from having a BCP and associated
Aside from having a BCP and associated 



