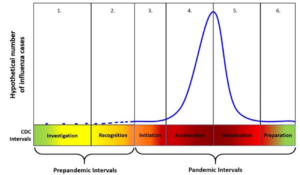
In a previous post, we discussed the role of the ISO in a pandemic and how he or she must make sure all routine tasks are still being completed; help the institution adapt to the new circumstances; and continue providing all products and services at an acceptable risk level.
While an institution may be prepared to continue business as usual, its third-party provider partners may not be on the same page. Like the bankers they support, third-party vendors are also experiencing the impact of the pandemic and are dealing with a variety of operational issues as well. Financial institutions must be able to perform effective vendor management during a crisis and develop alternative plans in the event a critical vendor may not be able to perform the services agreed upon.
Here are a few things the ISO must consider to effectively evaluate the institution’s vendors during a crisis like a pandemic:
Identify Vendor Risks
During a pandemic, the ISO must anticipate several different risk scenarios that can adversely impact the institution’s daily operations. With vendors, there are two interrelated key risk factors to consider:
- “Supply chain risk” is related to the interconnectivity among the entity and others. In a pandemic, critical vendors may receive an overload of requests for products and services from a variety of industries and may not be able to keep up with demand. For example, many financial institution employees have been working remotely due to Coronavirus and to keep the network secure, financial institutions have provided company laptops to staff. However, if the FI’s laptop provider runs out of inventory, the institution is then put in a difficult situation – if they allow the use of personal devices, they must still make sure all employees can work safely from home and ensure the network remains secure.
- “Cascading impact risk” is an incident affecting one entity or third-party service provider that then impacts other service providers, institutions, or sectors. For example, if the vendor that manages the bank’s perimeter security has a large case of absenteeism and an inadequate succession plan, real-time alerting may be negatively impacted, and the institution could be exposed.
Evaluating these risks with third-party vendors in advance will help ensure that they have the proper personnel redundancies in place, so these situations don’t impact the institution.
Managing Third-Party Risks
According to the Federal Financial Institution Examination Council (FFIEC), open communication and coordination with third parties, including critical service providers, is an important aspect of pandemic planning. A current SOC 2 report that covers the “availability” trust criteria is the best way to determine if the vendor has the capability to respond and recover its systems. In the absence of a SOC report, the first thing the ISO should request is a copy of the business continuity plan. Since the SOC report may not cover the service providers’ vendors (also referred to as sub-service providers), the ISO will also want to gain some awareness of the possibility of supply-chain risk. For example, how might a provider failure two to three layers deep affect the institution?
In addition to vendor business continuity plans, the ISO should ask additional questions about how the vendor is managing the pandemic. Here are a few examples:
- When was the last time you updated and tested your BCM plan? Have you incorporated the possibility of a failure of a critical sub-service provider?
- Is the likelihood and impact of a pandemic evaluated as a part of your risk assessment?
- How do you plan to continue providing services in the event of the loss of key employees?
- Have you been in communication with your critical third-party providers?
- Are you financially prepared to withstand a long-term pandemic event?
Critical third parties are often either overlooked or under-managed during normal circumstances, but because of the current high level of interdependency among financial institutions and their third-parties, operational events such as pandemics call for much closer scrutiny. Depending on responses received, ISOs may choose to accelerate their oversight efforts, revisit their vendor risk assessments, and make adjustments accordingly.
For more information on responding to pandemic events, view our pandemic resources.